Epic, which has been led by its 82-year-old founder Judy Faulkner for 46 years is best known for its dominance in the electronic health record software space, is pushing deeper into AI in a healthcare industry known for its complexities and…
Category: 5. Health
-

Tiny microbes may secretly rewire the brain before birth
- Microbes, or microorganisms, are all around us and play an important role in bodily functions. MSU researchers found that microbes can also impact brain development.
- This work is significant because modern obstetric practices like…
Continue Reading
-

AI Therapists Belong In The Back Office, Not The Chair.
AI therapy chatbots can’t replace therapists—but they can cut paperwork, train clinicians, and flag risk. Assistive uses help people; autonomy invites harm.
getty
Therapy has a supply problem. Depending on the dataset you pick, roughly half of…
Continue Reading
-
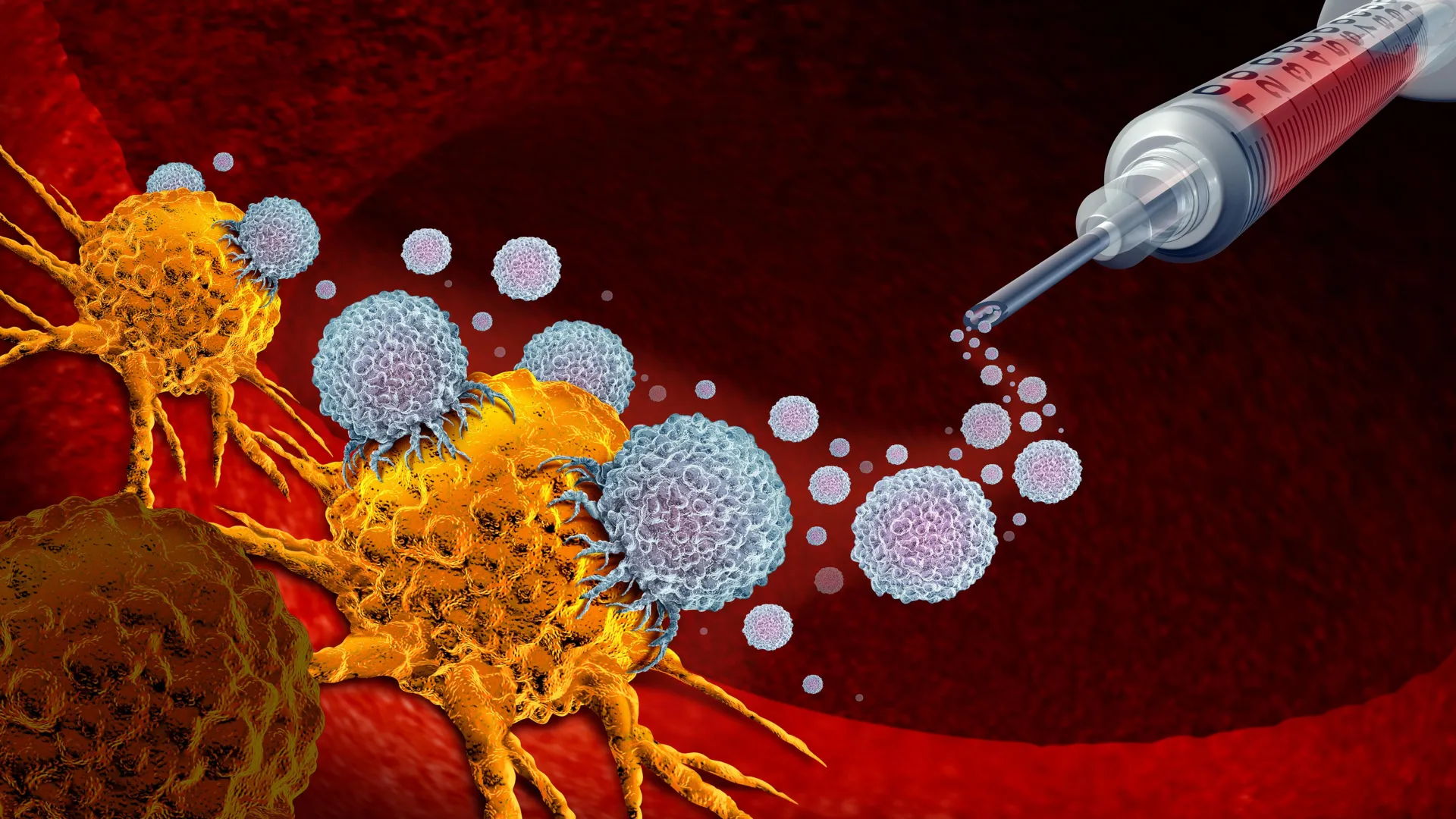
A new cancer vaccine just wiped out tumors in mice
An experimental mRNA vaccine boosted the tumor-fighting effects of immunotherapy in a mouse-model study, bringing researchers one step closer to their goal of developing a universal vaccine to “wake up” the immune system against cancer.
Published…
Continue Reading
-

This overlooked trait could explain anxiety and depression in millions
The meta-analysis of 33 studies, the first of its kind, looked at the relationship between sensitivity and common mental health problems such as depression and anxiety. Researchers found there was a significant, positive relationship between the…
Continue Reading
-
Even mild Covid may leave blood vessels five years older
A Covid infection, particularly in women, may lead to blood vessels aging around five years, according to research published today (August 18) in the European Heart Journal.
Blood vessels gradually become stiffer with age, but the new study…
Continue Reading
-

Is ketamine the answer for chronic pain? New findings cast doubt
The off-label use of ketamine to treat chronic pain is not supported by scientific evidence, a new Cochrane review has found.
Ketamine is an anaesthetic commonly used for procedural sedation and short-term pain relief. Ketamine is also frequently…
Continue Reading
-

Measles Outbreak In Texas Officially Has Ended, But The Threat Remains
Texas Department of State Health Services announced on Monday that the measles outbreak in West Texas has ended. But low vaccination rates mean that future outbreaks could occur. (Photo by Jan Sonnenmair/Getty Images)
Getty Images
The Texas…
Continue Reading
-
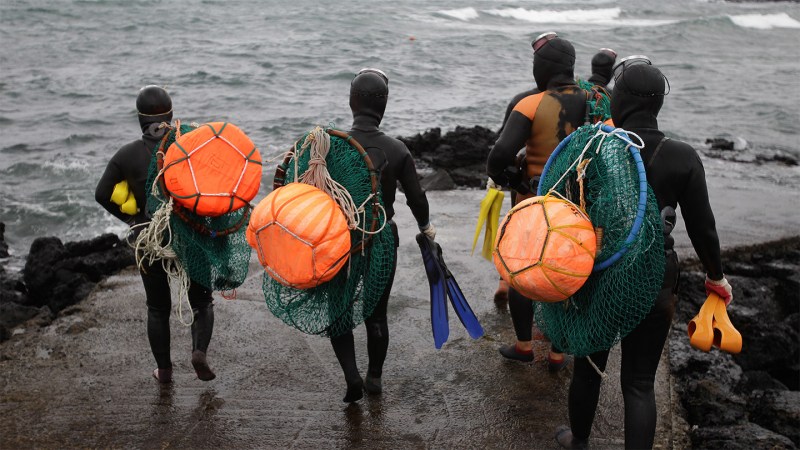

These female divers spend more time underwater than any other humans
The Haenyeo women who dive deep into the East China Sea to harvest sea urchins and shellfish spend the most time underwater of any humans ever studied — one to five hours a day, researchers report August 18 in Current…
Continue Reading